Portswigger - Access control vulnerabilities
Access Control vulnerabilities allow unauthorized users to access restricted resources or perform actions beyond their permitted scope. Such failures often result in unauthorized disclosure, modification, or deletion of data. Broken Access Control vulnerabilities currently hold the #1 spot on the OWASP Top 10 list (as of 2021).
In the context of web applications, access control relies on proper authentication and session management:
- Authentication confirms that the user is who they say they are
- Session management identifies if HTTP requests are made by the same user
- Access control determines whether the user is authorized to carry out the action that they are attempting to perform.
Exploitation
LAB 1 - Unprotected admin functionality
By appending /robots.txt to the end of the lab URL we can read the
content of the file.
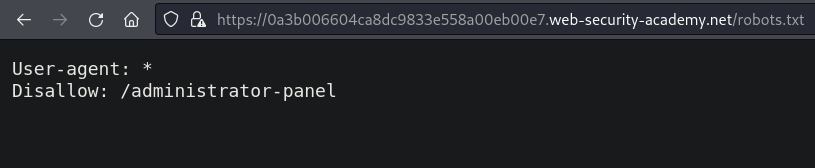
robots.txt implements the Robots Exclusion Standard
(RFC 9309) by telling the
search engine crawlers which URLs they can and can't access.
In this case, the hidden and unprotected administrator panel is being exposed
as robots.txt cannot be used to safeguard critical website functionality.
LAB 2 - Unprotected admin functionality with unpredictable URL
Some applications try to protect sensitive features with non-obvious URLs however, this approach, known as "security by obscurity", is not secure at all.
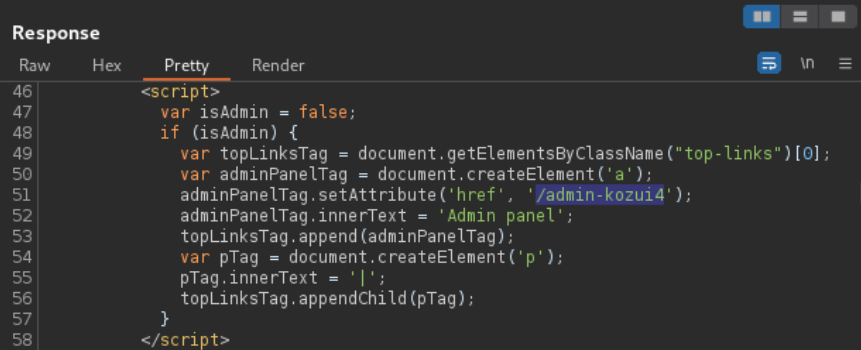
The webpage's source code contains a script that adds a link to the UI if the user is an administrator.
By appending /admin-kozui4 to the end of the lab URL we can access the hidden
and unprotected administrator panel.
LAB 3 - User role controlled by request parameter
Applications may determine the user's access rights at login, and then store this information in a user-controllable location, that could be:
# Hidden field
<input type="hidden" name="access_level" value="admin">
# Cookie
Cookie: Admin=true
# Preset query string parameter
https://insecure-website.com/login/home.jsp?admin=true
Accessing the lab's /admin panel, the HTTP GET request
sets the Admin=false cookie.
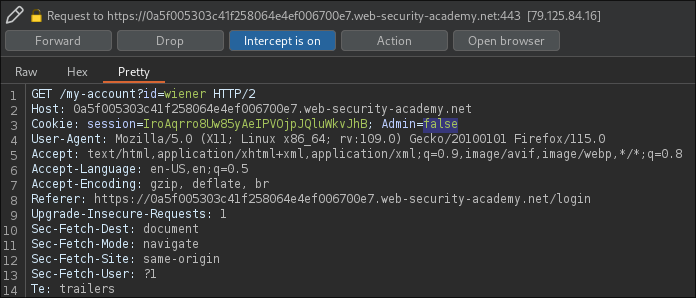
Setting the cookie's value to true gives us unintended access to the admin
panel.
LAB 4 - User ID controlled by request parameter, with unpredictable user IDs
While browsing the example blog we can stumble upon our victim's blog post titled "Identity Theft".
Clicking on carlos's username we can intercept their user GUID parameter
from the HTTP GET request.
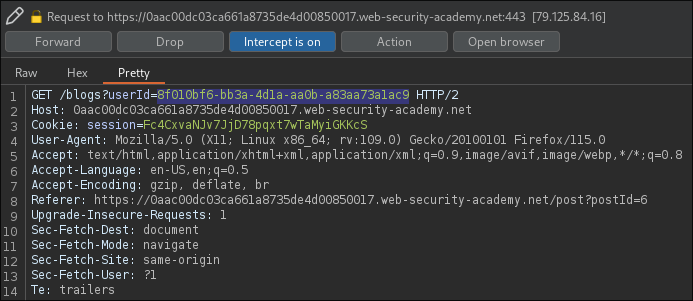
By modifying the user GUID sent to the server during our own login,
we can gain access to carlos's account without knowing their credentials.
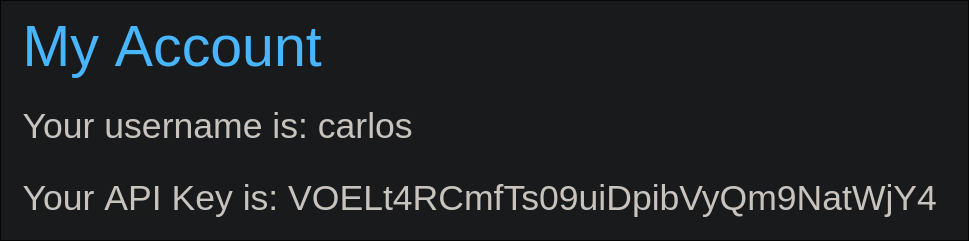
This process results in a horizontal privilege escalation, compromising the victim's secret API key.
LAB 5 - User ID controlled by request parameter with password disclosure
After logging in to our user account, the id parameter in the URL
can be modified from our username to administrator:
/my-account?id=administrator
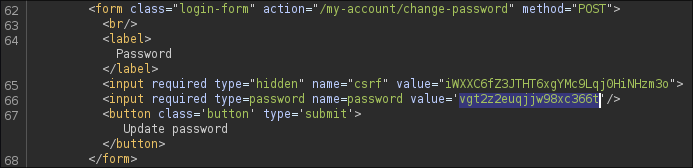
The captured HTTP response contains an input field pre-filled with the administrator's password in clear text.
Mitigation
To remediate Broken Access Control vulnerabilities, developers should
- implement proper authentication
- ensure the principle of Least Privilege
- use strong session management
- regularly audit access control policies
- conduct access control testing
- implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
